Receiving logs from Docker containers
Since FlowG has a Syslog endpoint, it can be used as a logging driver for Docker containers, allowing you to gather, parse, transform, refine and store or forward your logs to third-party services.
In this tutorial, we will setup FlowG as a logging driver for:
- specific Docker containers using the Docker CLI
- specific Docker containers using Docker Compose
- all Docker containers by configuring the Docker Daemon
NB: We will assume that FlowG is running on localhost with the Syslog endpoint listening on
UDP:5514. You can tune the configuration as you need.
Setting up a Docker container
Using the Docker CLI
Add the following parameters to your docker run command:
docker run --rm \
--log-driver=syslog \
--log-opt syslog-address=udp://localhost:5514 \
nginx:alpine
You can now check the logs in FlowG:
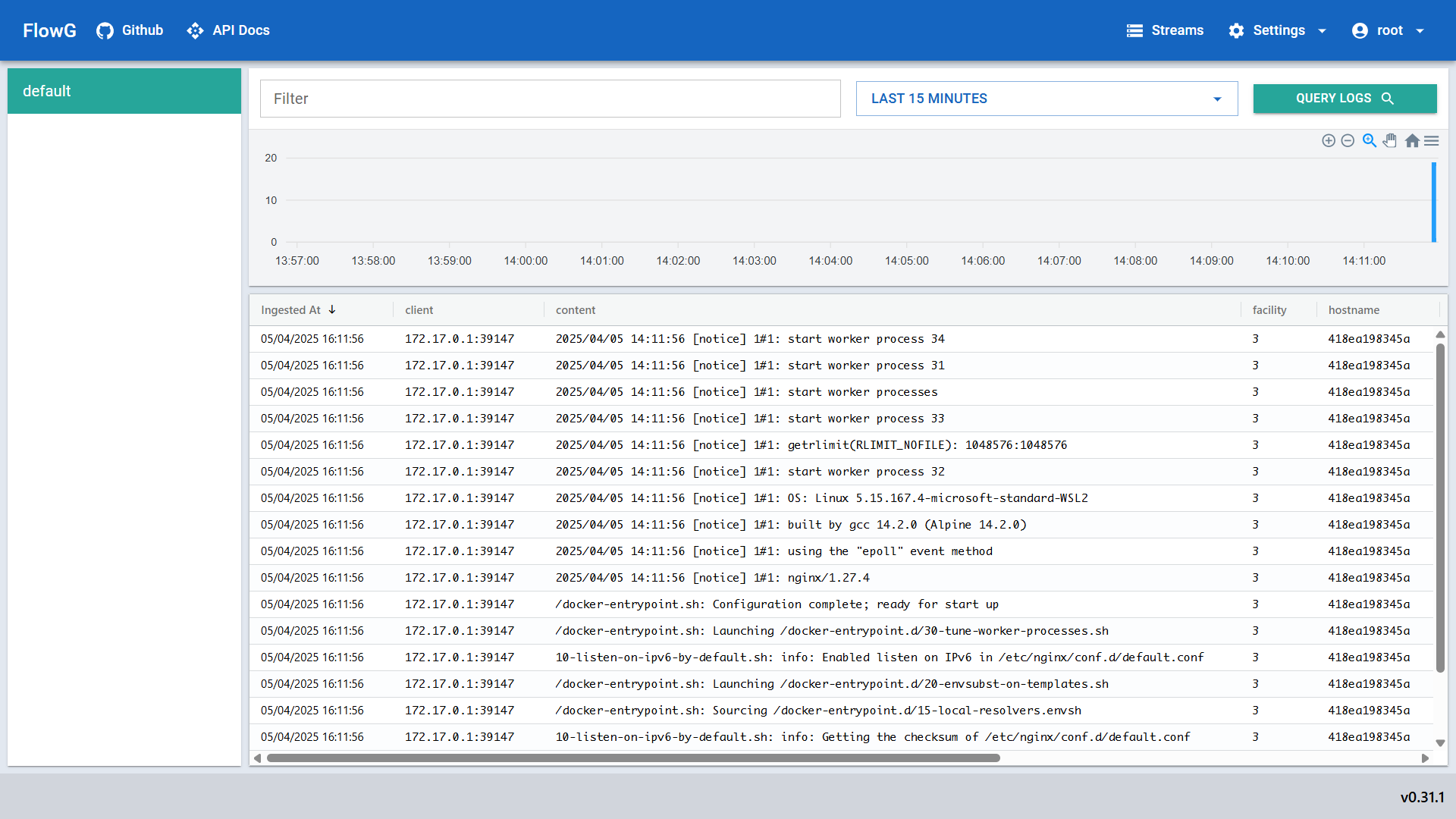
Using Docker Compose
You can also set the logging driver in your docker-compose.yml file:
services:
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
logging:
driver: syslog
options:
syslog-address: udp://localhost:5514
Then simply run:
docker compose up
Setting up the Docker Daemon
If you want to set the logging driver for all containers, you can configure the Docker Daemon to use FlowG as the default logging driver.
To do this, create or edit the /etc/docker/daemon.json file and add the
following:
{
"log-driver": "syslog",
"log-opts": {
"syslog-address": "udp://localhost:5514"
}
}
Then restart the Docker Daemon:
sudo systemctl restart docker
NB: You will need to recreate your containers for the new logging driver to take effect.