Forwarding logs to Datadog
Introduction
Datadog is a monitoring and analytics platform with great visualization capabilities. FlowG allows you to take advantage of Datadog's features by forwarding logs to it.
Setting up Datadog
DataDog provides an HTTP endpoint to receive logs (see the documentation). It expects in its payload the following properties:
| Property | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|
ddsource | string | nginx |
ddtags | string | env:prod,version:1.0 |
hostname | string | myhost |
service | string | myapp |
message | string | my log message |
All you need is to create an API Key in your Datadog account:
Setting up the FlowG pipeline
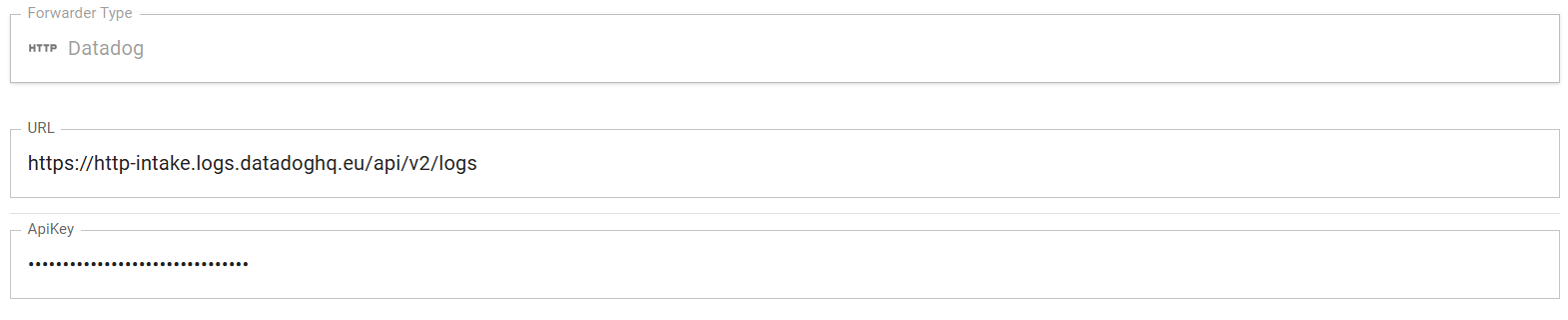
First, let's create a "Datadog Forwarder" named dd, with the following
configuration:
| Property | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| URL | https://http-intake.logs.datadoghq.com/api/v2/logs | This is the endpoint to send logs to |
| API Key | N/A | This is an API Key you created earlier |
⚠️ Important Notice
The API Key is tied to the "site" you use. The URL MUST match, otherwise you will receive a 403 error when trying to submit logs.
For example, if you are in Europe, the URL should be:
https://http-intake.logs.datadoghq.eu/api/v2/logs
Then, let's create a transformer named prepare-dd with the following code:
. = {
"ddtags": "test:flowg",
"ddsource": "logger",
"hostname": .hostname,
"service": "terminal",
"message": .content
}
This will setup the structure of the log record to the one expected by the Datadog HTTP Intake API.
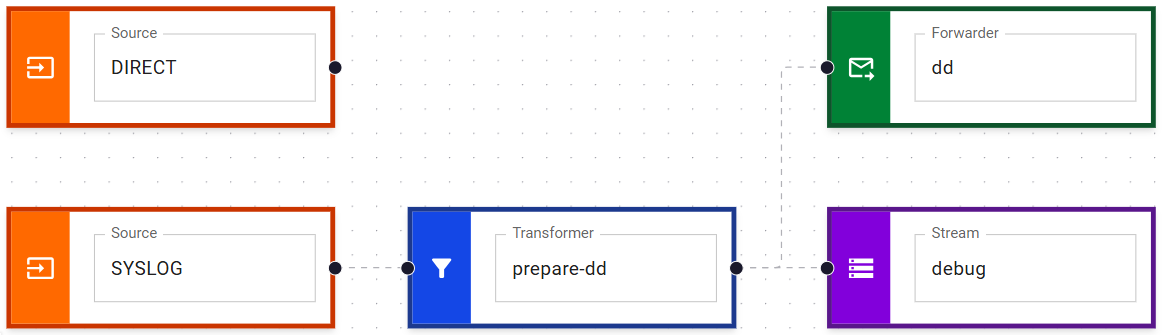
Finally, create a pipeline that transforms logs received via Syslog and forwards
them to the dd forwarder:
And that's it!
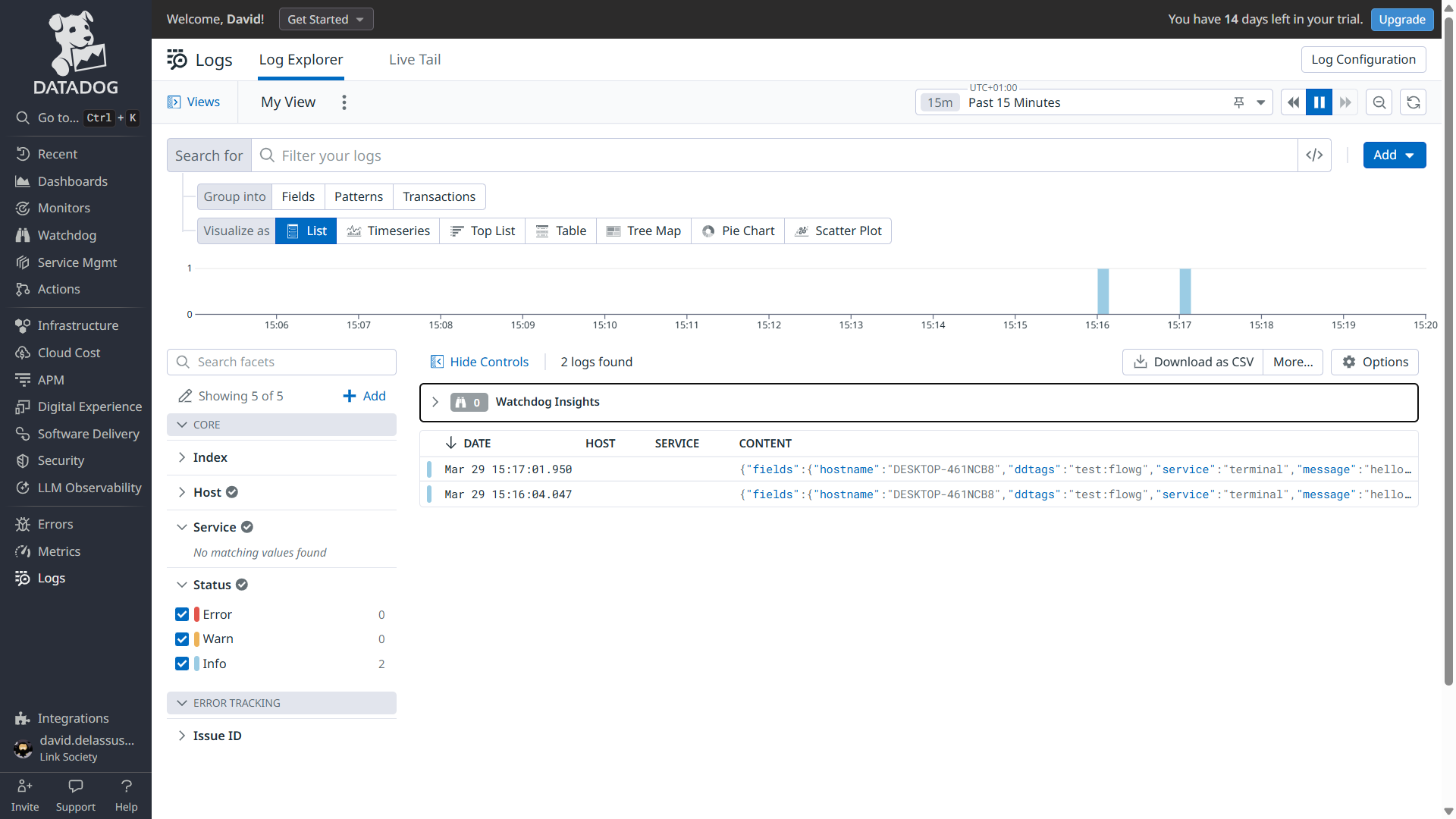
Testing
You can test the setup by sending a log to the pipeline using the logger
command:
logger -n localhost -P 5514 --rfc3164 -t myapp 'hello world'
You can then find your logs in Datadog at one of the following URLs depending on your region: