ELK (via API)
Introduction
FlowG allows you to view the logs your pipelines stored in streams. But the log viewer is pretty much barebones, as the main feature of FlowG is the pipeline itself. For that reason, you might want to forward logs to an ELK Stack, so that you can use Kibana to view your logs.
Fortunately, FlowG is able to forward logs to an ElasticSearch database.
In this tutorial, we will setup an ElasticSearch using Docker and a FlowG pipeline to forward logs to it.
Setting up ElasticSearch
First, run the Docker container:
docker run -d --name elasticsearch \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \
-e "ELASTIC_PASSWORD=changeme" \
-p 9200:9200 \
docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.15.3
Once started, create a user:
curl \
-k \
-u elastic:changeme \
-X POST https://localhost:9200/_security/role/index_manager \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"indices": [{"names": ["default"], "privileges": ["create_index","manage","read","write","view_index_metadata"]}]}'
curl \
-k \
-u elastic:changeme \
-X POST https://localhost:9200/_security/user/flowg \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"password": "changeme", "roles": ["index_manager"]}'
Then, fetch the CA certificate:
docker exec elasticsearch cat ./config/certs/http_ca.crt
Setting up the FlowG pipeline
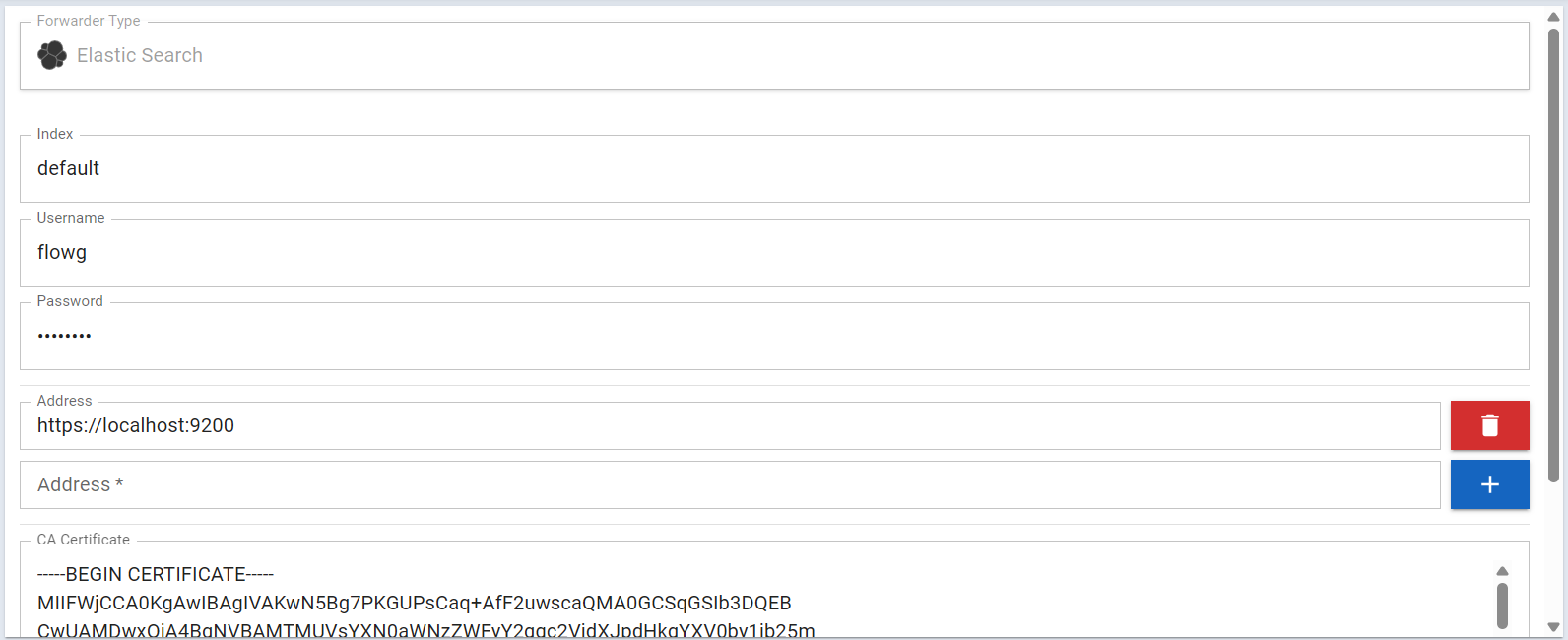
First, let's create an "Elastic Forwarder" named es, with the following
configuration:
| Property | Value | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Index | default | In which ElasticSearch index we will be writing logs |
| Addresses | https://localhost:9200 | URLs pointing to your ElasticSearch cluster |
| Username | flowg | The name of the user we just created |
| Password | ... | The password of the user we just created |
| CA Certificate | ... | Used to validate the ElasticSearch server certificate |
Then, create a pipeline that forwards logs to the es forwarder:
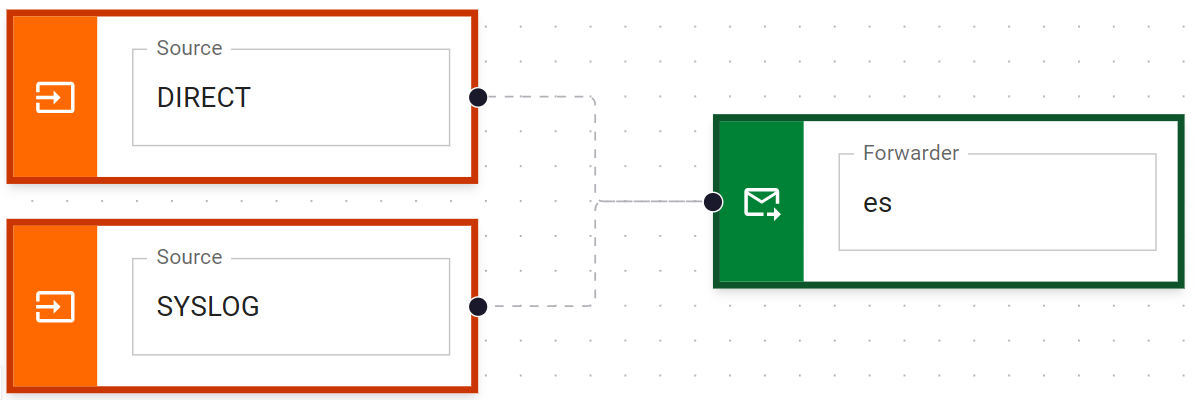
And that's it!
Testing
We can then run a simple query against ElasticSearch to check that our logs are being forwarded correctly:
logger -n localhost -P 5514 -t myapp 'hello world'
curl \
-k \
-u elastic:changeme \
-X GET "https://localhost:9200/default/_search?pretty" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"query": {"match_all": {}}}'
We should receive the following response:
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "default",
"_id" : "5HqEo5gBIAeBpdMlfIgf",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"timestamp" : "2025-08-13T13:00:25.296237816Z",
"fields" : {
"app_name" : "myapp",
"client" : "127.0.0.1:58598",
"facility" : "1",
"hostname" : "***",
"message" : "hello world",
"msg_id" : "-",
"priority" : "13",
"proc_id" : "-",
"severity" : "5",
"structured_data" : "[timeQuality tzKnown=\"1\" isSynced=\"1\" syncAccuracy=\"866000\"]",
"timestamp" : "2025-08-13 13:00:25.296014 +0000 UTC",
"tls_peer" : "",
"version" : "1"
}
}
}
]
}
}